The
java.util.Random class instance is used to generate a stream of pseudorandom numbers. The class uses a 48-bit seed, which is modified using a linear congruential formula.The algorithms implemented by class Random use a protected utility method that on each invocation can supply up to 32 pseudorandomly generated bits.
Commonly used methods of Random class
There is a list of commonly used Scanner class methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|
| protected int next(int bits) | This method generates the next pseudorandom number. |
| boolean nextBoolean() | This method returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed boolean value from this random number generator's sequence. |
| void nextBytes(byte[] bytes) | This method generates random bytes and places them into a user-supplied byte array. |
| double nextDouble() | This method returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed double value between 0.0 and 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
| float nextFloat() | This method returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed float value between 0.0 and 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
| double nextGaussian() | This method returns the next pseudorandom, Gaussian ("normally") distributed double value with mean 0.0 and standard deviation 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
| int nextInt() | This method returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed int value from this random number generator's sequence. |
| int nextInt(int n) | This method returns a pseudorandom, uniformly distributed int value between 0 (inclusive) and the specified value (exclusive), drawn from this random number generator's sequence. |
| long nextLong() | This method returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed long value from this random number generator's sequence. |
| void setSeed(long seed) | This method sets the seed of this random number generator using a single long seed. |
Screen shot
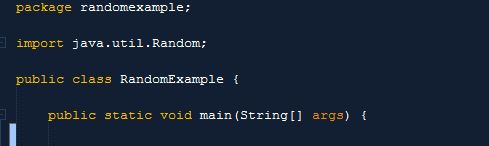
Source code


Comments
Post a Comment